Grade 1 Lv Diastolic Dysfunction Causes
Respiratory rate if abnormal may indicate cardiac decompensation or a primary lung disorder. Poor diastolic function typically Grade III - IV Diastolic heart failure.

Utility Of A Simple Algorithm To Grade Diastolic Dysfunction And Predict Outcome After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery
LVEF data for the group with reduced LVEF was retrieved from examinations performed up to 1 year before and up to 1 year after the index hospitalisation.

Grade 1 lv diastolic dysfunction causes. An echocardiogram has shown Grade 1 LV diastolic dysfunction consistent with age sclerotic aortic valve with no AS mild to moderate AR normal right heart. A dominance E may be dominant in the young or moderate diastolic dysfunction Variable. The identification of patients with HCM is sometimes still a challenge.
They may be systolic diastolic or continuous. The ASE recommends determining the grade of diastolic function based on the presence or absence of elevated LV filling pressures. Left ventricular failure causes shortness of breath and fatigue and right ventricular failure causes peripheral and abdominal fluid.
Significant mitral regurgitation MR is estimated to afflict 2 million Americans and is anticipated to increase in prevalence as the baby boomer population ages. Which decreased LV stroke volume. We are able to evaluate the grade of diastolic function and filling pressures by a combination of parameters.
The natural history of AS is one of slow progression. To minimize the inappropriate use of echocardiography in pregnant women one approach is to limit echocardiographic evaluation to pregnant women with a murmur only if they have 1 a history of underlying heart disease 2 definite cardiac symptoms 3 a grade 36 or greater systolic murmur or 4 a diastolic murmur. The rate increases in patients with heart failure Heart Failure HF Heart failure HF is a syndrome of ventricular dysfunction.
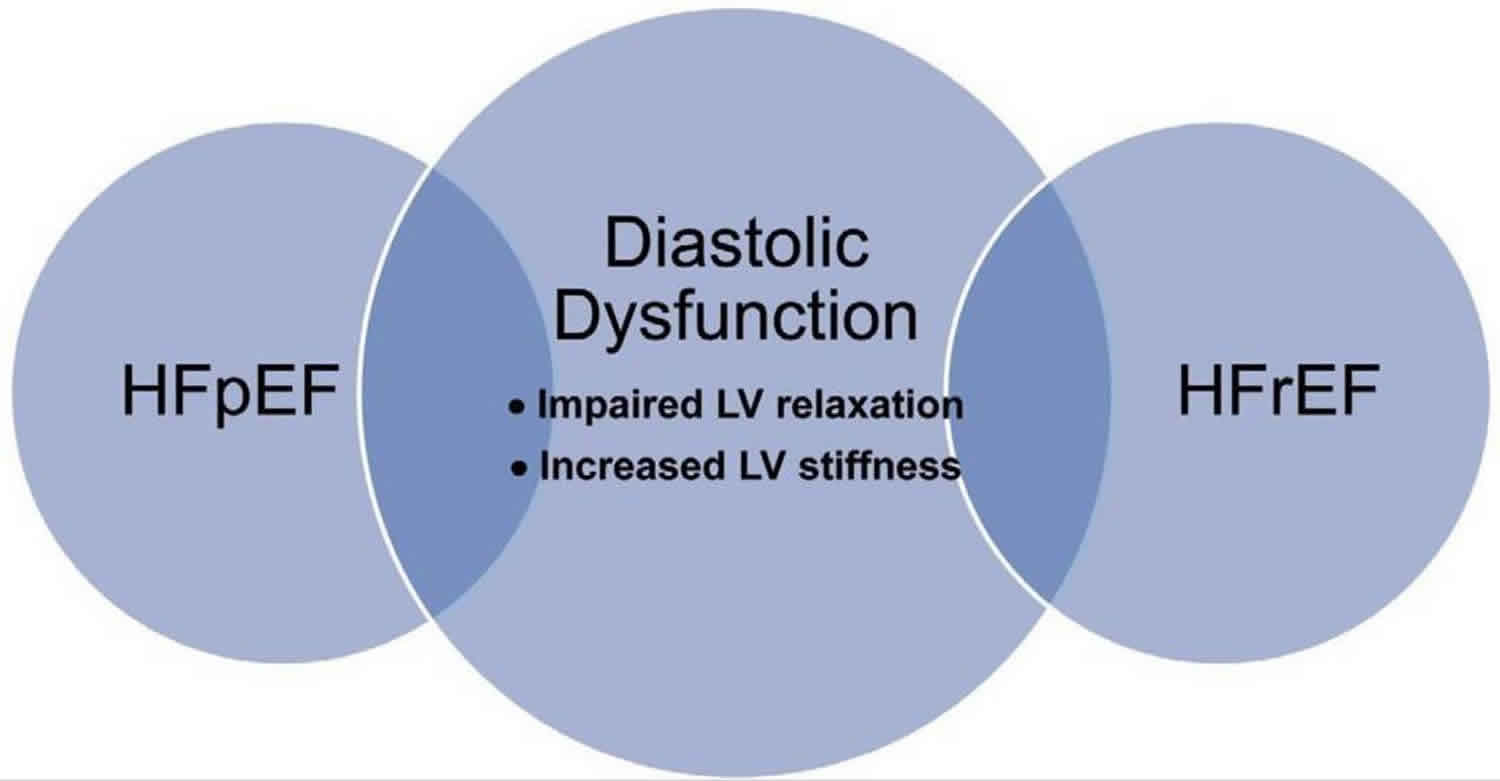
This may be measured by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. The latter increases the pressure gradient between the left atrium and the left ventricle and will act as a driving force to fill the ventricle during early diastole. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction HFpEF is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the left ventricle is maximally filled is normal defined as greater than 50.
Severe stenosis causes a transvalvular pressure gradient of 50 mm Hg in the presence of normal transvalvular flow ie normal LV function. Murmurs are graded in intensity on a scale of 1 to 6 see table Heart Murmur Intensity Heart Murmur Intensity Auscultation of the heart requires. Moreover the pathophysiology of the disease is complex because of left ventricular hyper-contractile state diastolic dysfunction ischemia and obstruction which can be coexistent in the same patient.
S dominant may be blunted in AF or diastolic dysfunction S dominant but may be blunted if eccentric MR may be blunted in AF or diastolic dysfunction S flow reversal. However there was a significant improvement in the primary outcome of cardiovascular dysfunction in the US study which was a composite of shock requiring vasopressor use and LV dysfunction in the combination therapy versus IVIG alone groups RR 056 95 CI 034-094. However abnormally low pressure gradients are found in conditions of LV dysfunction so the gradient alone is not a clear guide.
Those afflicted with RCM will experience decreased exercise tolerance fatigue jugular venous distention peripheral edema and ascites. I am morbidly obese with moderate sleep apnea. Chronic hypertension is one of the most common causes of diastolic heart failure.
Noncardiac causes include processes that increase the preload volume overload increase the afterload hypertension reduce the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood anemia or increase demand sepsis. As a result the heart gets more muscular and stiffer which affects its ability to relax during the resting stages of the cardiac cycle when it fills with blood. 1 Approximately 10 of people 75 years of age have significant MR 1 and these patients have decreased survival regardless of whether MR is caused by a primary leaflet abnormality 2 or is secondary to left ventricular LV.
Alternatively if the EF is less than 50 dobutamine stress echocardiography may reveal severe aortic stenosis or prompt evaluation for other causes of LV dysfunction. Hello doctor thank you for your valuable time I had an echo back in December of 2017 it showed mild left diastolic dysfunction grade 1 with an rvsp of 37. The intensity of S 1 depends on the integrity and pliability of valvular cusps the length of the PR interval which governs the velocity of valve closure the strength of ventricular contraction the presence or absence of valvular stenosis or regurgitation the position of the valve leaflets at end.
My blood pressure is typically 14075. They are graded by intensity and are described by their location and when they occur within the cardiac cycle. Cardiac causes include arrhythmias tachycardia or bradycardia structural heart disease and myocardial dysfunction systolic or diastolic.
At a median follow-up of 35 years 48 subjects died. Arrhythmias and conduction blocks are common. High blood pressure.
In order to allow proper amount of filling during diastole the filling pressures increase. Pathophysiology Congestive Heart Failure - Diastolic Diastolic dysfunction occurs when the left ventricular myocardium is noncompliant and not able to accept blood return in a normal fashion from the left atrium. High blood pressure over a long time means that the heart has to work harder to pump blood through the body.
If a grade 3 dysfunction is not affected by the maneuver the condition is classified as grade 4 diastolic dysfunction irreversible restrictive filling. Opportunistic infection in AIDS ALL Cerebellar medulloblastoma 388. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HCM is one of the most common inherited cardiomyopathy.
LV function on TOE during AFAFL was defined as normal if LVEF was 50 and the grade of LV dysfunction as categorised as mild moderate and severe if LVEF was 4549 3044 and. They did a repeat echo in July of 2018 it showed left diastolic dysfunction grade 2 rvsp of 53. When aorotic valve closes earlier than pulmonic valve More to the Right heart Less to the left - Can cause a split in s2 - only heard in pulmonic valve area you can hear the mitral and tricuspid components separately this is a split S2.
4414 Pseudonormal filling pattern - grade 2 diastolic dysfunction Progressive diastolic dysfunction causes left atrial pressure to rise. This can be a normal physiologic change with aging of the heart or result. Murmurs are produced by blood flow turbulence and are more prolonged than heart sounds.
Nephrotic syndrome blackhispanic and obese adults Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. Two-dimensional and Doppler methods for assessment of LV diastolic function Nagueh et al. E wave dominant E velocity 15 ms EROA cm 2.
In patients with grade 1 diastolic dysfunction main symptom is exertional dyspnea. Typically S 1 is a high-pitched sound best heard with the diaphragm of the stethoscope. As well as anti rejection drugs I am on Amlodopine 10 mg and Atorvastatin 20 mg.
Opening snap and diastolic rumble Mitral stenosis chronic rheumatic fever Can lead to pulmonary HTN 392. Shortens LV systole and allows the aortic valve to close a bit earlier. In the Mayo Clinic cross-sectional community survey of 2042 adults 45 years of age 21 percent had mild diastolic dysfunction 7 percent had moderate diastolic dysfunction and 1 percent had severe diastolic dysfunction.
Many elderly subjects and patients with hypertension or LV hypertrophy have Doppler echocardiographic evidence of impaired diastolic function but do not have any symptoms of heart failure at rest.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/grade-1-diastolic-dysfunction-5194119-FINAL-21f474a9180245efb402cd48e53e4456.jpg)
Grade 1 Diastolic Dysfunction Symptoms Treatments

Diastolic Dysfunction Learn The Heart

Causes Of Diastolic Dysfunction Download Table

Diastolic Dysfunction Definition Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Grades Of Diastolic Dysfunction Download Table

Scheme For Grading Diastolic Dysfunction Av Average La Left Download Scientific Diagram
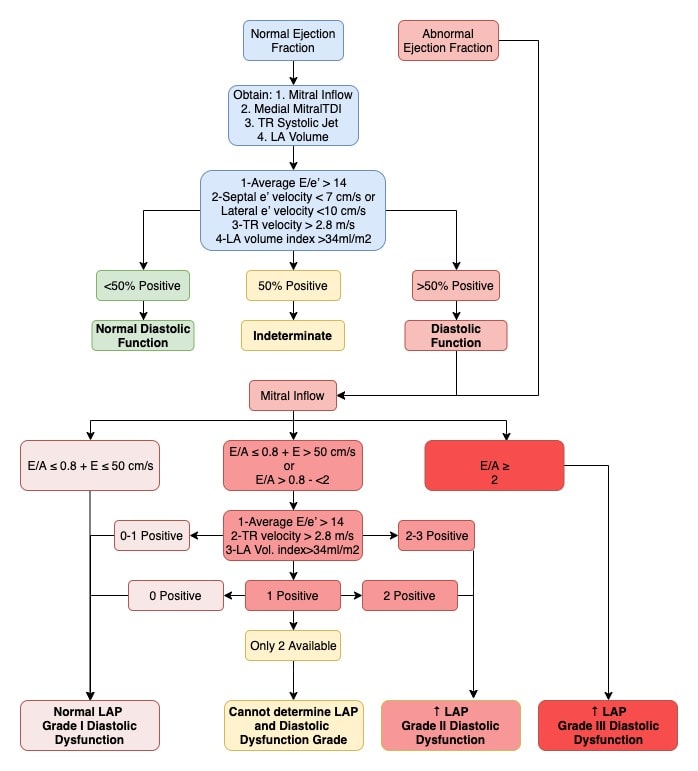
Diastolic Dysfunction Cardio Guide

Why Diastolic Dysfunction Raises Death Risk Cleveland Clinic

Assessment Of Diastolic Function By Echocardiography Ecg Echo
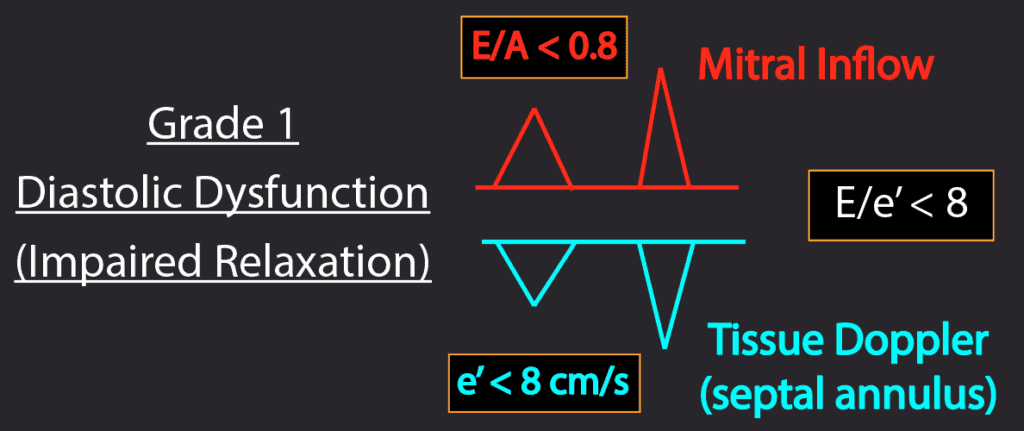
How To Measure And Grade Diastolic Dysfunction Using Echocardiography Pocus 101

Hypertension And Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Mayo Clinic Proceedings

Key Predisposing Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction Increased Download Scientific Diagram

Pathophysiology And Echocardiographic Diagnosis Of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography

Diastolic Function Diastolic Dysfunction 123 Sonography
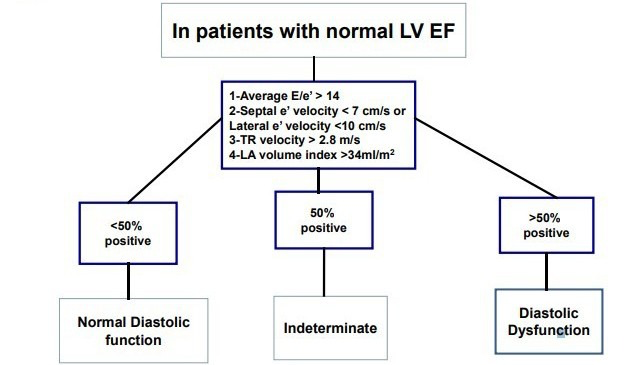
Common Mistakes Diastolic Dysfunction 123 Sonography

Echocardiographic Evaluation Of Diastolic Function Is Of Limited Value In The Diagnosis And Management Of Hfpef Journal Of Cardiac Failure

How To Measure And Grade Diastolic Dysfunction Using Echocardiography In 2021 Diagnostic Medical Sonography Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Cardiology
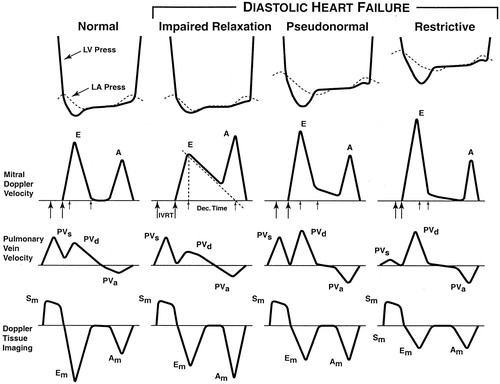
Common Mistakes Diastolic Dysfunction 123 Sonography
Diastolic Dysfunction Definition Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment